This is an old revision of the document!
Milestone 2
Starting with week 3, we are going to work with pfSense, an open source firewall with documentation that can be consulted here.
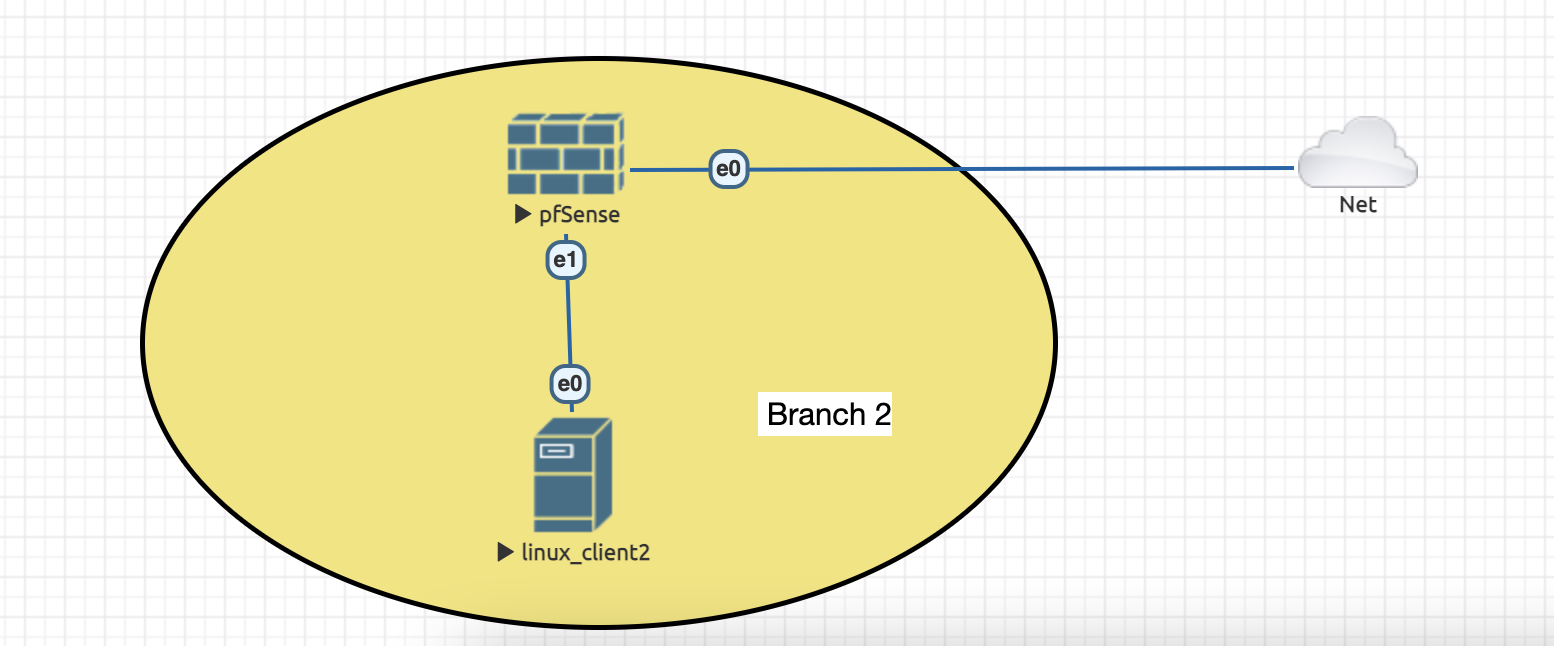
Topology we are going to use this week:
1. Download the iso.gz file: https://www.pfsense.org/download/ (latest version tested 2.6)
2. Copy downloaded archive to eve-ng instance using scp
3. Go through the steps from eve-ng website: https://www.eve-ng.net/index.php/3380-2/ (use as folder name pfsense-2.7.0). Make sure to power off the node instance (after installation is completed) and save the snapshot as a new base image in path /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu
4. Power on the instance again, set the ip addresses for vtnet0 (WAN, using DHCP) and vtnet1 (LAN, choose default subnet 192.168.1.0/24).
5. Create a new Linux node (like done previously here: https://ocw.cs.pub.ro/courses/sred/setup_lab_remote#virtual_machine_access) and connect it to e1 from pfsense.
6. Look over the commands from console menu: https://docs.netgate.com/pfsense/en/latest/config/console-menu.html. Go to shell and find the ip address for interface vtnet0 (it should be in subnet 10.6.0.0/16).
7. Change the mac address to a custom one, from cli:
# select shell (8 key) # change mac address based on your eve_ng instance ip ifconfig vtnet0 link 50:00:00:$SECOND_BYTE:$THIRD_BYTE:$FORTH_BYTE # example: for 10.6.0.10, use mac address 50:00:00:06:00:10
Then, run again dhclient vtnet0 and get the new ip address assigned.
8. Try to access the webGUI interface using browser. Does it? Why not? (hint: https://advanxer.com/2019/12/pfsense-enabling-administration-via-the-wan-interface/).
9. At last, login using default credentials (https://docs.netgate.com/pfsense/en/latest/usermanager/defaults.html) and go through the setup part (do not forget to save the new password!).
10. Go to Interfaces > WAN > MAC Address, add also there the mac address from above, then Save and apply changes. This way your mac will be permanently saved.
11. Add a new rule to permit traffic to WAN interface from your tunnel ip address (check GlobalProtect). Revert steps done previously, on step 6 (hint: use again shell and same binary).
12. Start Linux machine and make sure it receives a private ip from 192.168.1.0/24.
13. At last, add a new NAT rule to have Internet access from that computer.