This is an old revision of the document!
Lab 6. Fortigate Virtual Domains (VDOMs)
Setup
On the last lab, remember that we used an evaluation license (used for a maximum of 1 vCPU and 2 GB RAM) available for only 15 days (see here more).
user@host:# ssh -l root $YOUR_EVE_NG_IP # default passwd is student root@SRED:~# df -h | grep SRED--vg /dev/mapper/SRED--vg-root 67G 52G 12G 83% / # if you have more than 60G used, delete old labs from eveng webui # (for each node you create, there are new qcow2 files using the based ones)
As an alternative, you can delete from this path /opt/unetlab/tmp the files created for each node, but the first option is the recommended one.
Licensing
From this lab on, we will need to have a licensed VM. As we have only 1 license available, we will reuse it for all fortigate firewalls using the following steps: 0. We will blackhole the default route after the license is marked as VALID, then create a route only for client user ip (which will mostly be the same for all firewalls) 1. Find which private ip have the packages that are received by firewall. Go to cli and check packets:
FGT60 # diagnose sniffer packet port1 icmp Using Original Sniffing Mode interfaces=[port1] filters=[icmp] 11.597280 10.128.0.20 -> 10.3.0.35: icmp: echo request 11.597395 10.3.0.35 -> 10.128.0.20: icmp: echo reply # from you host, send an imcp echo-req to the specific port1 ip address
See above that source ip address is the internal one 10.128.0.20, which we will use later to fwd packets via 10.3.255.254 (def gateway).
2. From the browser, go to IP_FORTIGATE/ng/system/vm/license and ask me at this point to upload the license.
3. Wait for the firewall to reboot, then access the machine again via vnc to make sure the mgmt ip was not changed.
FGT60 # show system interface ? # find here port1 ip
4. Remeber that this device has an implicit default route to 10.3.255.254 with AD = 5.
FGT60 # get router info routing-table details [...] S* 0.0.0.0/0 [5/0] via 10.3.255.254, port1
Now, go to cli (via vnc) and create 2 new static routes:
# create a new static route with dest 10.128.0.20 FGT60 # config router static FGT60 (static) # edit 1 new entry '1' added FGT60 (1) # set dst 10.128.0.20 255.255.255.255 FGT60 (1) # set gateway 10.3.255.254 FGT60 (1) # set distance 10 FGT60 (1) # set device port1 FGT60 (1) # end # overwrite now the old default route from fw with AD = 1 FGT60 # config router static FGT60 (static) # edit 2 new entry '2' added FGT60 (2) # set dst 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 FGT60 (2) # set distance 1 FGT60 (2) # set blackhole enable FGT60 (2) # end # from this point on, all requests to Internet are blackholed (the exception is the packets sent to client ip 10.128.0.20, which traffic originates from remote students).
5. At last, go to webui using your browser and start the lab.
Exercises
Find on moodle course the pdf file for the Fortinet Exercises. As we will work with VDOMs, go to chapter 3 and start the tasks.
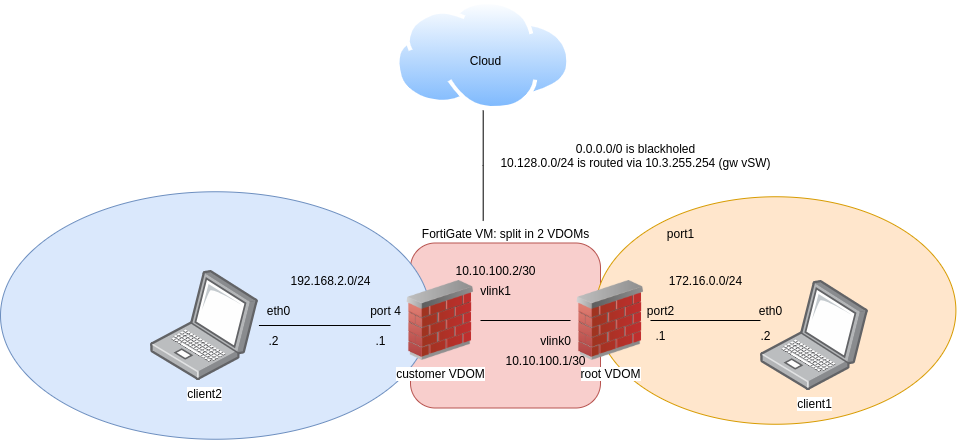
The topology that we will use:
The difference in our case is that client2 (which needs to be linked with port4 to fw) will not access Internet (as all traffic to def route is sinkholed) and client1 instead (on which we will configure at the end an ad hoc server).
Next, I will give you some tips or different config you need to do:
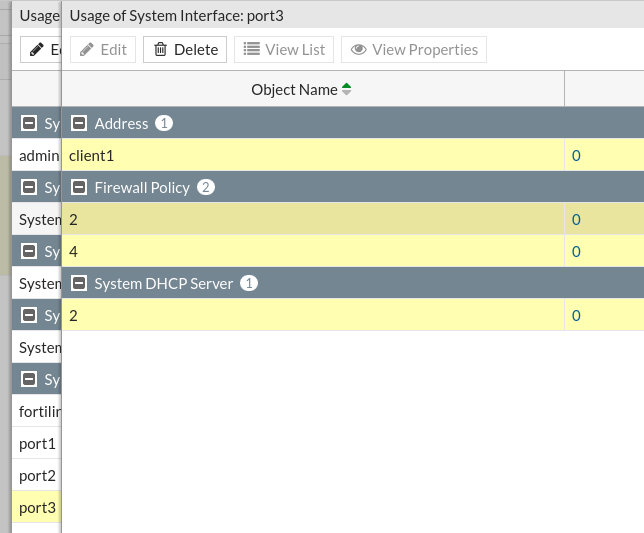
The solution here is to clear all references to a port (a reference = a configuration like policy rule, dhcp server, interface that is attached to that interface). Go to Global mode > System > VDOM > root > double click to number from Ref. column (number of references for that vdom), then find interface port4 > double click again to Ref. value, then select each subvalue with Ctrl and Delete all Refs.
Try again to change vdom for port4 to customer.
Exercise 1:
- you can skip from page 63 the config revisions revert
- to enable VDOM on a FGW, you need to go to cli:
config system global
set vdom-mode multi-vdom # this is a hidden command
end
Then, go logout, login again and check the webui.
- instead of port3 for customer VDOM, we will use port4 (the one remained from the last lab not configured). If you already have a machine attached to port3, shutdown the firewall and reattach it to 4.
- port 4 is using network 192.168.2.0/24 with 192.168.2.1 for gw (fw), dhcp server with pool 192.168.2.2-192.168.2.254 and http, https, ping enabled for admin access
- to access the firewall using the customer credentials, we will need to access webui from client2: after client2 gets an ip from dhcp server (should be 192.168.2.2), go to Mozilla > https://192.168.2.1 and try to login with customer account
Exercise 2:
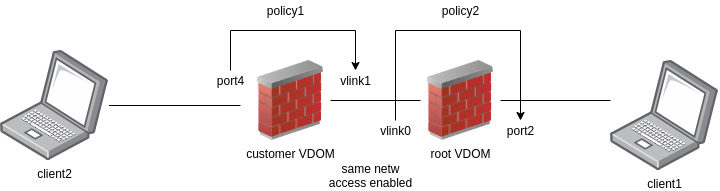
- the mapping are the following: port4 - vlink1 (for customer vdom) and vlink0 - port2 (for root vdom)
- to test the connection from client2 to client1 (we cannot do the ex from page 75), try to ping 172.16.0.2 and create a simple http server:
eve@ubuntu:/$ cd /tmp; mkdir test_http; echo "CONFIDENTIAL" > test_http/important_data eve@ubuntu:/$ cd test_http eve@ubuntu:/$ python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8080
Then, go to client2 and access this resource:
eve@ubuntu:/$ curl 172.16.0.2:8080/important_data CONFIDENTIAL