Lab04. Cuckoo sandboxing
Objectives
- Investigate a possible malware using automatic tools
- Use the cuckoo sandbox automated malware analysis system
- Introduction to basic Linux command line
Topology
For this exercise you will need the malware archive.
You will also need a Linux environment with Cuckoo sandbox installed and a running Windows VM. One can be downloaded from here.
Tasks
01. [10p] Virtual machine setup
You will need to have Linux VM (we have tested with Ubuntu 20.04) and then install the Cuckoo sandbox on top of it. You can access Cuckoo sandbox from a browser, and to limit the impact of the malware analysis process please do so from the same VM (i.e. install a graphical server and a browser on the Linux VM).
$startx (to start the graphical interface)
After the installation you need to power on the cuckoo sandbox system using the following commands. To verify that cuckoo sandboxing is running open the hxxp://127.0.0.1:8000 into a browser.
$cuckoo web runserver $cuckoo -d (!!! do not run as sudo)
Next, inside your Linux VM one needs to run a second VM with Windows. This one is used by the Cuckoo framework to do the automatic malware analysis. Follow the tutorials available and make sure that the Windows VM is available. In the case of misconfigured guest VM (i.e., the Windows 7 VirtualBox VM), you can reset it to the initial configuration. 1
- Delete any existing snapshots.
- Power on the virtual machine.
- Create a new snapshot
VBoxManage snapshot "win7cuckoo" take "original" --pause
- Power of the virtual machine
VBoxManage controlvm "win7cuckoo" poweroff
- Restore the virtual machine to use the previously created snapshot.
VBoxManage snapshot "win7cuckoo" restorecurrent
All this setup is already done in the following VM https://drive.google.com/file/d/14-7DqZ1jNKuqxr73Wk8TcTylRl7tNKNk/view?usp=sharing
02. [30p] Malware analysis
To start the malware investigation, submit the received files using the dashboard and select Analyze from the “Configure your Analysis” page. Please configure a 500 seconds Timeout to allow enough time for execution and make sure that the package type is “exe” from the left-side panel for a proper lunch.
- Once the process has started, you should be able to see the progress in the terminal where the cuckoo daemon was lunched. Moreover, the Windows 7 pre-configured virtual machine should be started, and the malware launched.
- Observe that the python agent within the Windows 7 has launched the malware and is monitoring it. You should also be able to see the random mouse movements. Why is this happening?
03. [20p] Report overview
After the report has been generated, you should be able to answer the following questions.
- What is the executable file format? What is the Original Filename of the executable?
- What is the hash (preferable SHA2 family) of the malware? Can you find it on hxxp://www.virustotal.com?
- What command is executed to allow access to all files?
- Which DNS records are recorded during the analysis?
- What registry entries does the malware add?
04. [30p] More result analysis
All the monitored actions are stored by Cuckoo in the “.cuckoo” configuration folder under the storage directory.
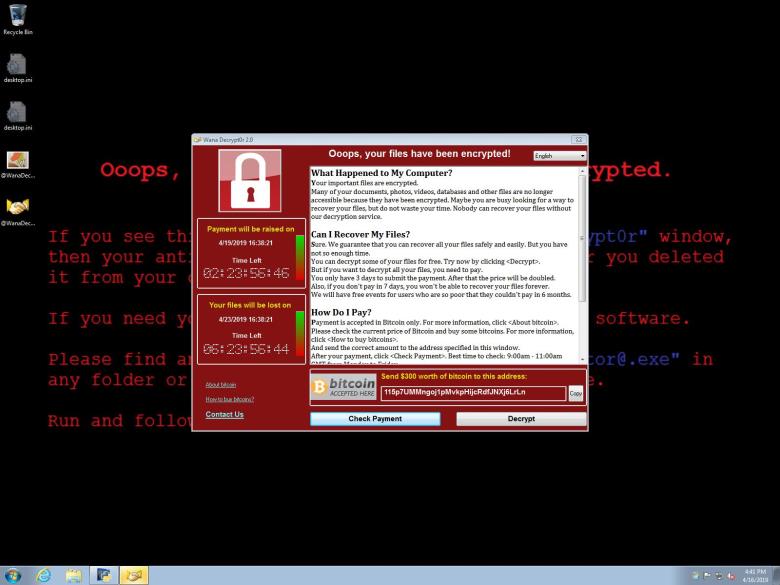
- Find in what languages is the support message from the malware available.
- Which files were encrypted during the process?
- Have a look at the captured traffic using Wireshark.
05. [10p] Custom rules for automated analysis
Cuckoo sandbox has a lot of extra tools that it can use for deeper analysis, including snort IDS, IDA for binary or Yara for signature matching. The Yara rules can be run against the binary itself, against the memory dump or accessed URLs. In this exercise we are going to use the Yara rules available on the following github repository. Just copy them in the yara configuration directory and re-run the analysis.
06. [Bonus 10p] Custom rules for automated analysis
Redo the analysis using the https://any.run/ platform.